1. 【说明】
下面的程序先构造Point类,再顺序构造Ball类。由于在类Ball中不能直接存取类Point中的xCoordinate及yCoordinate属性值,Ball中的toString方法调用Point类中的toStrinS方法输出中心点的值。在MovingBsll类的toString方法中,super.toString调用父类Ball的toString方法输出类Ball中声明的属性值。
【Java代码】
//Point.java文件
public class Point{
private double xCoordinate;
private double yCoordinate;
public Point(){}
public Point(double x,double y){
xCoordinate=x;
yCoordinate=y;
}
public String toStrthg(){
return"("+Double.toString(xCoordinate)+","
+Double.toString(yCoordinate)+")";
}
//other methods
}
//Ball.java文件
public class Ball{
private
;//中心点
private double radius;//半径
private String color;//颜色
public Ball(){}
public Ball(double xValue, double yValue, double r){
//具有中心点及其半径的构造方法
center=
;//调用类Point中的构造方法
radius=r;
}
public Ball(double xValue, double yValue, double r, String c){
//具有中心点、半径和颜色的构造方法
;//调用3个参数的构造方法
color=c;
}
public String toString(){
return "A ball with center"+center.toString()
+",radius "+Double.toString(radius)+",color"+color;
}
//other methods
}
class MovingBall
{
private double speed;
public MovingBall(){}
public MoyingBall(double xValue, double yValue, double r, String c, double s){
;//调用父类Ball中具有4个参数的构造方法
speed=s;
}
public String toString(){
return super.toString()+",speed"+Double.toString(speed);
}
//other methods
}
public class test{
public static void main(String args[]){
MovingBall mb=new MovingBall(10,20,40,"green",25);
System.out.println(mb);
}
}
(1) Point center
(2) new Point(xValue,yValue)
(3) this(xValue,yValue,r)
(4) extends Ball
(5) super(xValue,yValue,r,c)
[解析] 在类Ball的有参数构造函数中,对成员变量center通过调用Point类的构造方法初始化,而center在类Ball中尚未声明。结合注释可得空(1)是将center变量声明为Point对象引用,故空(1)应填Point。空(2)是调用Point类的构造函数,根据题意,此处应将xValue和yValue作为参数调用类Point的有参数构造函数,故空(2)应填new Point(xValue,yValue)。
根据注释,空(3)是调用类Ball的有3个参数的构造方法,而其所在方法本身就是类Ball的一个构造方法,因此可用this来调用自身的构造方法,故空(3)应填this(xValue,yValue,r)。
根据题述“在MovingBall类的toString方法中,super.toString调用父类Ball的toString方法输出类Ball中声明的属性值”,可知类MovingBall是类Ball的子类,因此空(4)应填extends Ball。
根据注释,空(5)是调用父类Ball中具有4个参数的构造方法,通过super关键字实现,故空(5)应填super(xValue,yValue,r,c)。
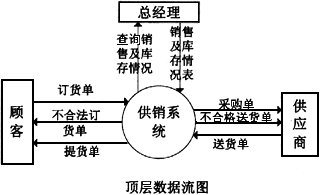
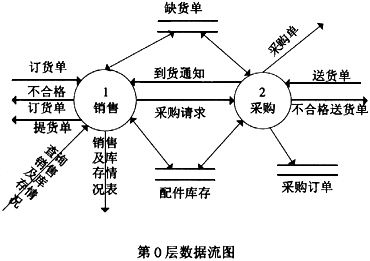
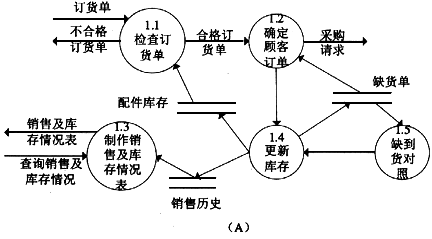
 aixi中有许多系数为零时,可用一个单链表来存储,每个节点存储一个非零项的指数和对应系数。
aixi中有许多系数为零时,可用一个单链表来存储,每个节点存储一个非零项的指数和对应系数。